- 22 11 53 600
- Mon-Fri: 900 - 2000 • Sat: 900-1300
- kontakt@hipermedica.com.pl
Home page - Services
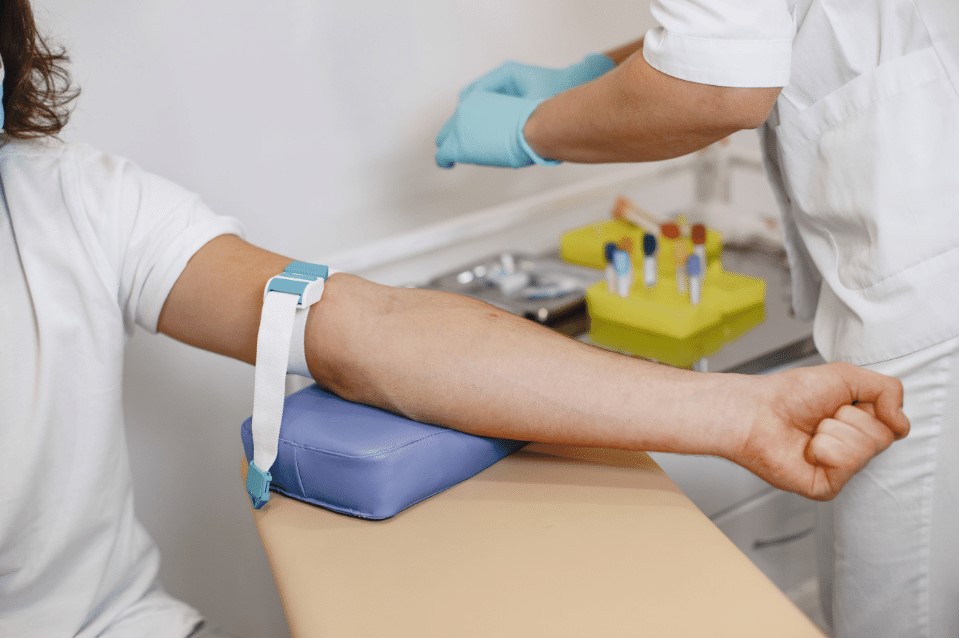
Diagnostic and therapeutic procedures
Our experienced doctors and state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment allow us to carry out procedures with the utmost care and safety for patients. In our clinic we focus on an individual approach to each patient and provide full support and care throughout the diagnostic and treatment process.
We invite you to take advantage of our services and to learn more about our full range of diagnostic and treatment procedures related to bone marrow and blood tests available below.
Choose the treatment you are interested in and find out the details
Bloodletting is a procedure involving the removal of a certain volume of blood from the body. One time, depending on the clinical situation, 200-450 ml of blood is dropped, and the dropped volume is replaced by administering saline solution.
The bloodletting procedure includes:
- medical consultation
- qualification for bloodletting
- bloodletting
- intravenous infusion of saline (0.9% NaCl)
Bone marrow examination is a basic method in hematological diagnosis, necessary for making a diagnosis and evaluating the effects of treatment of many diseases. A physician performs the procedure. Bone marrow biopsy, so-called aspiration biopsy, is performed with a thin needle and allows the collection of bone marrow cells for cytological examination, but also highly specialized cytogenetic or molecular studies. There are no significant contraindications to performing an aspiration biopsy, except for inflammatory or infectious lesions of the skin at the site of the potential prick.
The examination is performed in the supine position or on the side (biopsy of the iliac plate – near the posterior superior iliac spine) or on the back (biopsy of the sternum – near the handle of the sternum). The procedure takes several to several minutes. After the biopsy site is decontaminated, local anesthesia is administered, and then the actual procedure begins – the biopsy needle is inserted sequentially through the skin, connective tissues and muscles, and then into the spongy substance of the bone, which is the proper place for bone marrow aspiration. Some patients may experience discomfort during and after the procedure despite the local anesthesia used, as it is impossible to anesthetize the marrow cavity. After aspiration of the bone marrow, the biopsy needle is removed, the puncture site is compressed and secured with a sterile dressing, and the puncture site is recommended to be compressed. Thirty minutes after the procedure, the biopsy site is inspected and, if there are no complications, the patient is allowed to leave the medical facility.
Complications of the procedure are relatively rare, and the procedure itself is considered safe. The most commonly observed complications include pain and bleeding from around the biopsy site, skin irritation and the development of local inflammation. Serious complications are observed very rarely. These include, in the case of a sternum biopsy, its puncture, damage to the arterial vessels and the heart below the bone, and damage to the pelvic vessels in the case of a hip plate biopsy. However, these complications are observed very rarely, mainly in patients with advanced bone disease (osteoporosis, plasmocytic myeloma, after surgery). Needles with special puncture depth limiters are used to reduce the risk of their occurrence. In addition, allergy or anaphylactic shock to the local anesthesia or disinfectants may also occur.
It is a bone marrow biopsy using a thick needle, which, in addition to the aspiration of liquid marrow, allows the extraction of a small piece of bone for histopathological examination. Trepanobiopsy is essential for making a diagnosis in many hematological diseases. It is also used to monitor treatment. The procedure’s site is the posterior superior iliac spine region, similar to a bone marrow aspiration biopsy. In the case of trephine biopsy, an additional part of the procedure is to make a small incision in the skin to allow the insertion of the biopsy needle.
Bloodletting is a procedure involving the removal of a certain volume of blood from the body. One time, depending on the clinical situation, 200-450 ml of blood is dropped, and the dropped volume is replaced by administering saline solution.
The bloodletting procedure includes:
- medical consultation
- qualification for bloodletting
- bloodletting
- intravenous infusion of saline (0.9% NaCl)
Bone marrow examination is a basic method in hematological diagnosis, necessary for making a diagnosis and evaluating the effects of treatment of many diseases. A physician performs the procedure. Bone marrow biopsy, so-called aspiration biopsy, is performed with a thin needle and allows the collection of bone marrow cells for cytological examination, but also highly specialized cytogenetic or molecular studies. There are no significant contraindications to performing an aspiration biopsy, except for inflammatory or infectious lesions of the skin at the site of the potential prick.
The examination is performed in the supine position or on the side (biopsy of the iliac plate – near the posterior superior iliac spine) or on the back (biopsy of the sternum – near the handle of the sternum). The procedure takes several to several minutes. After the biopsy site is decontaminated, local anesthesia is administered, and then the actual procedure begins – the biopsy needle is inserted sequentially through the skin, connective tissues and muscles, and then into the spongy substance of the bone, which is the proper place for bone marrow aspiration. Some patients may experience discomfort during and after the procedure despite the local anesthesia used, as it is impossible to anesthetize the marrow cavity. After aspiration of the bone marrow, the biopsy needle is removed, the puncture site is compressed and secured with a sterile dressing, and the puncture site is recommended to be compressed. Thirty minutes after the procedure, the biopsy site is inspected and, if there are no complications, the patient is allowed to leave the medical facility.
Complications of the procedure are relatively rare, and the procedure itself is considered safe. The most commonly observed complications include pain and bleeding from around the biopsy site, skin irritation and the development of local inflammation. Serious complications are observed very rarely. These include, in the case of a sternum biopsy, its puncture, damage to the arterial vessels and the heart below the bone, and damage to the pelvic vessels in the case of a hip plate biopsy. However, these complications are observed very rarely, mainly in patients with advanced bone disease (osteoporosis, plasmocytic myeloma, after surgery). Needles with special puncture depth limiters are used to reduce the risk of their occurrence. In addition, allergy or anaphylactic shock to the local anesthesia or disinfectants may also occur.
It is a bone marrow biopsy using a thick needle, which, in addition to the aspiration of liquid marrow, allows the extraction of a small piece of bone for histopathological examination. Trepanobiopsy is essential for making a diagnosis in many hematological diseases. It is also used to monitor treatment. The procedure’s site is the posterior superior iliac spine region, similar to a bone marrow aspiration biopsy. In the case of trephine biopsy, an additional part of the procedure is to make a small incision in the skin to allow the insertion of the biopsy needle.
Preparation for bone marrow aspiration biopsy/trepanobiopsy and general remarks
- - Report about 15-20 minutes in advance to read the consent for the study and fill out the necessary documents
- - It is a good idea to reserve about 1-1.5 hours of time for the procedure
- - Have the results of peripheral blood count and coagulation system (APTT, PT, fibrinogen) - valid for 1-3 days
- - Eat a light meal about 2 hours before the procedure - fasting is not recommended
- - Prepare a list of medications you are taking - some medications, including antiplatelet drugs (Acard, Aclotin, Plavix, Briloque, among others) or anticoagulants (Acenocoumarol, Warfin, Xarelto, Pradaxa, Eliquis, low molecular weight heparins) may lead to prolonged bleeding after the procedure hence it may be necessary to modify their intake after consultation with your doctor
- - If you are allergic to the drug or have a history of allergic or anaphylactic reactions, it is necessary to inform the staff in advance
- - The protective dressing after the procedure can be removed the following day in the absence of bleeding
- - In case of deterioration of general condition after the procedure, or bleeding from the wound, it is necessary to report to the ED (Hospital Emergency Department) for examination and medical supplies
Subscribe to our Newsletter
-
Aleja Komisji Edukacji Narodowej 94 / U5
02-777 Warsaw, Poland -
22 11 53 600
725 620 777 - kontakt@hipermedica.com.pl
Important links
Opening hours
Mon - Fri:
09.00 - 20.00
Saturday:
09.00 - 13.00
Sunday:
Close
© 2023 HiperMedica. All rights reserved.
