- 22 11 53 600
- Mon-Fri: 900 - 2000 • Sat: 900-1300
- kontakt@hipermedica.com.pl
Home page - Services
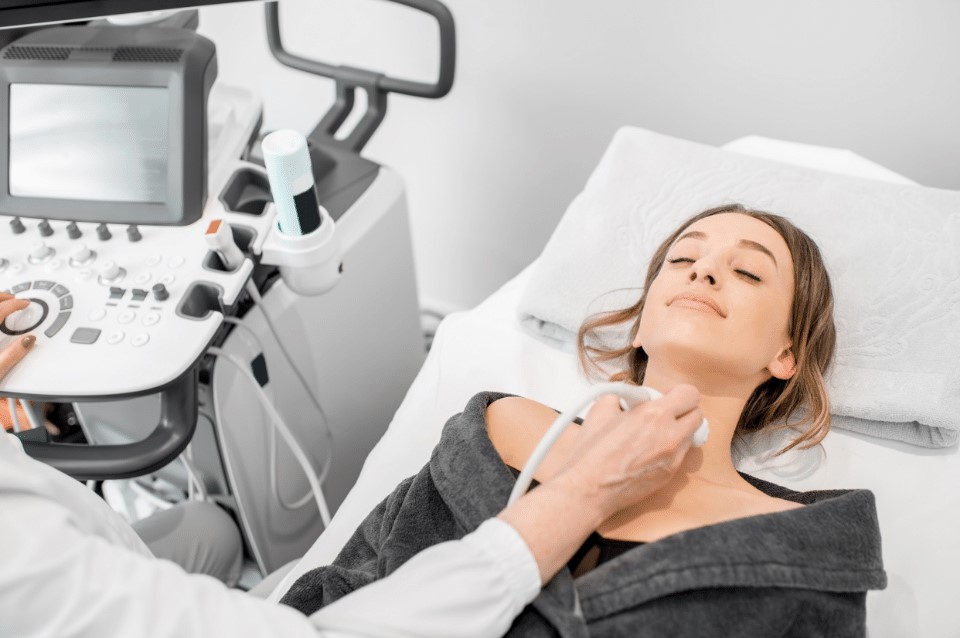
Diagnostic and imaging tests
Diagnostic and imaging tests are an important part of medical diagnosis, allowing us to assess a patient’s condition accurately. Below you will find descriptions of the tests we perform at our facility.
Our medical clinic offers a wide range of diagnostic and imaging tests, carried out by experienced specialists, to provide our patients with comprehensive medical care.
Select the study you are interested in and find out the details
- Ultrasound examination (USG)
- Doppler ultrasound of the portal system
- Echocardiography examination
- Electrocardiographic examination
- Spirometric examination
- Lab tests
The ultrasound examination uses high-frequency sound waves, known as ultrasound. The examination is safe, non-invasive and painless. Ultrasound examination is one of the best and safest methods of diagnostic imaging. It can be performed repeatedly without any intervals between examinations.
With ultrasound, it is possible to evaluate many areas of the body and organs, including the abdomen. In the abdominal ultrasound, the liver, including the gallbladder with bile ducts, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands, urinary bladder, and pelvic organs (uterus and ovaries in women, prostate in men) can be evaluated. In addition to the abdominal cavity, the ultrasound examination can evaluate, among other things:
• soft tissues
• thyroid
• testicles
• lymph nodes
• breast gland
Most ultrasound examinations do not require prior preparation, but in the case of abdominal ultrasound, adequate preparation is already advisable due to the need to evaluate the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract. Therefore, it is advisable to abstain from meals for 6-8 hours before the examination. He recommends abstaining from smoking and chewing gum at least 24 hours before the scheduled examination. Two days before the examination, it is recommended not to eat bloating foods, i.e. cabbage, peas, beans or carbonated beverages. However, it is advisable to drink water and, about an hour before the test, drink more water and refrain from urinating. A full urinary bladder allows its accurate assessment.
At our institution, ultrasound examinations are performed by Dr. Jerzy Wojtowicz (ultrasound of soft tissues and parenchymal organs, abdomen, lymph nodes, thyroid, urinary system, prostate) and Dr. Maciej Wysocki (abdominal examination).
Doppler ultrasound of the portal system
Portal System Doppler ultrasound evaluates the liver’s blood vessels. It is useful in diagnosing problems related to blood flow in the portal system, such as portal hypertension. This test helps detect blood clots, circulation problems, and other liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or splenic enlargement. It is also used in liver transplant patients.
What are the indications for a liver portal Doppler study?
– Cirrhosis of the liver
– HCV and HBV infection
– Alcohol-induced liver damage
– Suspected portal hypertension
– Steatosis of the liver
– Liver fibrosis
– Esophageal varices
– Ascites (fluid in the abdominal cavity)
– Enlargement of the spleen
Purpose of the examination
The main goal is to detect problems with portal circulation, such as abnormal blood flow in the portal vein, splenic vein, and superior mesenteric vein. The doctor also looks for signs of collateral circulation (i.e., alternative blood flow pathways), which may indicate portal hypertension. Other problems that can be diagnosed with the test
– Developmental abnormalities of the portal system
– Thromboses or other changes in the portal vein and its branches
– Calcification of the walls of the veins
– Presence of gas in the vessels of the portal system
– Arteriovenous fistulas (abnormal connections between vessels)
– Portal-systemic connections after surgery
– Heart failure (right side)
– Effects of drugs on circulation
– Complications after liver transplantation
How to prepare for the test?
– The patient must be fasting for 6 hours before the test.
– Do not chew gum one hour before the test.
– The day before the examination, an easily digestible diet is recommended.
– On the day of the examination and the day before, take e.g. Espumisan (3 times a day, 2 capsules each) to reduce intestinal gas to facilitate the examination.
ECHO of the heart is an ultrasound examination that evaluates the structure and function of the heart and large blood vessels and surrounding tissues. It is one of the main diagnostic methods used in cardiac diagnostics. It allows the diagnosis of heart defects (congenital and acquired), ischemic disease (myocardial infarction), pulmonary embolism, inflammatory diseases of the heart and pericardium, cardiomyopathies, aortic aneurysms, causes of heart failure, syncope. It is indispensable for cardiac evaluation before oncological treatment with cardiotoxic (heart-damaging) potential. In the outpatient clinic Hipermedica, an echo examination can be performed using the most modern methods of assessing myocardial function. Analysis of longitudinal strain of the left ventricle (GLS, global longitudinal strain) is used in the best cardiology centers in the world, in Polish conditions almost unavailable in ambulatory care. GLS is a sensitive parameter used to assess cardiac damage at a very early stage. It is used to diagnose heart failure, cardiomyopathy, ischemic heart disease, amyloidosis or cardiotoxicity associated with cancer treatment. This test detects cardiac dysfunction early in the disease, making it possible to implement appropriate treatment quickly.
Dr. Jaroslaw Kepski performs heart echo examination at our facility.
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a non-invasive and painless test used to assess the heart’s electrical function. It is used to diagnose arrhythmias, palpitations and chest pain. The test uses electrodes placed on the surface of the patient’s chest and upper and lower extremities, which collect electrical impulses that are then converted into an ECG recording. The test is often recommended before surgical treatment. In addition, the indication for an ECG is chest pain/discomfort, palpitations, sensations of irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, and fainting.
Holter ECG testing allows for long-term (24-hour) monitoring of ECG recordings. Its main task is to diagnose arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, bradycardia, ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias).
As part of the test, the patient is given a small recording device (the size of a cell phone) connected by wires to three electrodes placed on the chest. During monitoring, the patient must avoid getting the device wet and taking baths and showers; other than these exceptions, the day’s cycle should proceed naturally. After 24 hours, the recording device should be returned to the clinic so a specialist can read and interpret the data.
Spirometry is the most important functional test of the respiratory system, allowing objective assessment of lung function. During spirometry, the volume of air exhaled and inhaled into the lungs is assessed. The test involves breathing in an appropriate manner through the mouthpiece of the apparatus. Indications for spirometry testing are suspected asthma (a useful test for diagnosis) or COPD (necessary for the diagnosis of this disease) and monitoring their course assessment of lung function in patients with interstitial diseases (such as pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis and others). Before the test, to obtain objective and reliable results, you should:
- stop smoking for 24 hours (at least 2 hours before the test)
- do not consume alcohol 4 hours before the test
- do not drink coffee and tea 4 hours before the test
- do not eat too much food 2 hours before the examination
- wear loose, non-restrictive clothing that allows free movement of the chest and diaphragm (avoid ties, corsets loosen the belt of your pants)
- notify staff of medications taken
- do not take (if possible) inhaled drugs, including:
- short-acting beta-mimetics 8 hours before the test (e.g. Ventolin, Salbutamol)
- long-acting beta-mimetics 12 hours before the test (e.g., Formoterol, Salmeterol)
- short-acting anticholinergics (e.g., Atrovent) 6 hours before the examination
- long-acting anticholinergics (Spiriva) 7 days before the test.
Dr. Justyna Kępska performs spirometry examinations in our institution
Laboratory tests, including blood and urine, are among the most commonly performed diagnostic tests. They help detect abnormalities in the functioning of our body. They are one of the first steps leading to disease diagnosis and health assessment. The most important of the laboratory tests is blood count. In addition to morphology, the evaluation of the parameters of the capacity of the liver, kidneys or other organs is widely used in medicine.
In order to meet the needs of our patients, we offer a wide range of laboratory tests in our collection center at very attractive, competitive prices. To see our price range, click here.
In addition to basic blood and urine tests, highly specialized tests for clotting disorders (embolism, thrombophilia, hemorrhagic diathesis) and genetic testing are available at our facility.
Please contact us and our collection center, which is open on Tuesdays and Thursdays from 9:00 – 12:00.
- Ultrasound examination (USG)
- Doppler ultrasound of the portal system
- Echocardiography examination
- Electrocardiographic examination
- Spirometric examination
- Lab tests
The ultrasound examination uses high-frequency sound waves, known as ultrasound. The examination is safe, non-invasive and painless. Ultrasound examination is one of the best and safest methods of diagnostic imaging. It can be performed repeatedly without any intervals between examinations.
With ultrasound, it is possible to evaluate many areas of the body and organs, including the abdomen. In the abdominal ultrasound, the liver, including the gallbladder with bile ducts, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands, urinary bladder, and pelvic organs (uterus and ovaries in women, prostate in men) can be evaluated. In addition to the abdominal cavity, the ultrasound examination can evaluate, among other things:
• soft tissues
• thyroid
• testicles
• lymph nodes
• breast gland
Most ultrasound examinations do not require prior preparation, but in the case of abdominal ultrasound, adequate preparation is already advisable due to the need to evaluate the gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract. Therefore, it is advisable to abstain from meals for 6-8 hours before the examination. He recommends abstaining from smoking and chewing gum at least 24 hours before the scheduled examination. Two days before the examination, it is recommended not to eat bloating foods, i.e. cabbage, peas, beans or carbonated beverages. However, it is advisable to drink water and, about an hour before the test, drink more water and refrain from urinating. A full urinary bladder allows its accurate assessment.
At our institution, ultrasound examinations are performed by Dr. Jerzy Wojtowicz (ultrasound of soft tissues and parenchymal organs, abdomen, lymph nodes, thyroid, urinary system, prostate) and Dr. Maciej Wysocki (abdominal examination).
Doppler ultrasound of the portal system
Portal System Doppler ultrasound evaluates the liver’s blood vessels. It is useful in diagnosing problems related to blood flow in the portal system, such as portal hypertension. This test helps detect blood clots, circulation problems, and other liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or splenic enlargement. It is also used in liver transplant patients.
What are the indications for a liver portal Doppler study?
– Cirrhosis of the liver
– HCV and HBV infection
– Alcohol-induced liver damage
– Suspected portal hypertension
– Steatosis of the liver
– Liver fibrosis
– Esophageal varices
– Ascites (fluid in the abdominal cavity)
– Enlargement of the spleen
Purpose of the examination
The main goal is to detect problems with portal circulation, such as abnormal blood flow in the portal vein, splenic vein, and superior mesenteric vein. The doctor also looks for signs of collateral circulation (i.e., alternative blood flow pathways), which may indicate portal hypertension. Other problems that can be diagnosed with the test
– Developmental abnormalities of the portal system
– Thromboses or other changes in the portal vein and its branches
– Calcification of the walls of the veins
– Presence of gas in the vessels of the portal system
– Arteriovenous fistulas (abnormal connections between vessels)
– Portal-systemic connections after surgery
– Heart failure (right side)
– Effects of drugs on circulation
– Complications after liver transplantation
How to prepare for the test?
– The patient must be fasting for 6 hours before the test.
– Do not chew gum one hour before the test.
– The day before the examination, an easily digestible diet is recommended.
– On the day of the examination and the day before, take e.g. Espumisan (3 times a day, 2 capsules each) to reduce intestinal gas to facilitate the examination.
ECHO of the heart is an ultrasound examination that evaluates the structure and function of the heart and large blood vessels and surrounding tissues. It is one of the main diagnostic methods used in cardiac diagnostics. It allows the diagnosis of heart defects (congenital and acquired), ischemic disease (myocardial infarction), pulmonary embolism, inflammatory diseases of the heart and pericardium, cardiomyopathies, aortic aneurysms, causes of heart failure, syncope. It is indispensable for cardiac evaluation before oncological treatment with cardiotoxic (heart-damaging) potential. In the outpatient clinic Hipermedica, an echo examination can be performed using the most modern methods of assessing myocardial function. Analysis of longitudinal strain of the left ventricle (GLS, global longitudinal strain) is used in the best cardiology centers in the world, in Polish conditions almost unavailable in ambulatory care. GLS is a sensitive parameter used to assess cardiac damage at a very early stage. It is used to diagnose heart failure, cardiomyopathy, ischemic heart disease, amyloidosis or cardiotoxicity associated with cancer treatment. This test detects cardiac dysfunction early in the disease, making it possible to implement appropriate treatment quickly.
Dr. Jaroslaw Kepski performs heart echo examination at our facility.
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a non-invasive and painless test used to assess the heart’s electrical function. It is used to diagnose arrhythmias, palpitations and chest pain. The test uses electrodes placed on the surface of the patient’s chest and upper and lower extremities, which collect electrical impulses that are then converted into an ECG recording. The test is often recommended before surgical treatment. In addition, the indication for an ECG is chest pain/discomfort, palpitations, sensations of irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, and fainting.
Holter ECG testing allows for long-term (24-hour) monitoring of ECG recordings. Its main task is to diagnose arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, bradycardia, ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias).
As part of the test, the patient is given a small recording device (the size of a cell phone) connected by wires to three electrodes placed on the chest. During monitoring, the patient must avoid getting the device wet and taking baths and showers; other than these exceptions, the day’s cycle should proceed naturally. After 24 hours, the recording device should be returned to the clinic so a specialist can read and interpret the data.
Spirometry is the most important functional test of the respiratory system, allowing objective assessment of lung function. During spirometry, the volume of air exhaled and inhaled into the lungs is assessed. The test involves breathing in an appropriate manner through the mouthpiece of the apparatus. Indications for spirometry testing are suspected asthma (a useful test for diagnosis) or COPD (necessary for the diagnosis of this disease) and monitoring their course assessment of lung function in patients with interstitial diseases (such as pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis and others). Before the test, to obtain objective and reliable results, you should:
- stop smoking for 24 hours (at least 2 hours before the test)
- do not consume alcohol 4 hours before the test
- do not drink coffee and tea 4 hours before the test
- do not eat too much food 2 hours before the examination
- wear loose, non-restrictive clothing that allows free movement of the chest and diaphragm (avoid ties, corsets loosen the belt of your pants)
- notify staff of medications taken
- do not take (if possible) inhaled drugs, including:
- short-acting beta-mimetics 8 hours before the test (e.g. Ventolin, Salbutamol)
- long-acting beta-mimetics 12 hours before the test (e.g., Formoterol, Salmeterol)
- short-acting anticholinergics (e.g., Atrovent) 6 hours before the examination
- long-acting anticholinergics (Spiriva) 7 days before the test
Dr. Justyna Kępska performs spirometry examinations in our institution
Laboratory tests, including blood and urine, are among the most commonly performed diagnostic tests. They help detect abnormalities in the functioning of our body. They are one of the first steps leading to disease diagnosis and health assessment. The most important of the laboratory tests is blood count. In addition to morphology, the evaluation of the parameters of the capacity of the liver, kidneys or other organs is widely used in medicine.
In order to meet the needs of our patients, we offer a wide range of laboratory tests in our collection center at very attractive, competitive prices. To see our price range, click here.
In addition to basic blood and urine tests, highly specialized tests for clotting disorders (embolism, thrombophilia, hemorrhagic diathesis) and genetic testing are available at our facility.
Please contact us and our collection center, which is open on Tuesdays and Thursdays from 9:00 – 12:00.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
-
Aleja Komisji Edukacji Narodowej 94 / U5
02-777 Warsaw, Poland -
22 11 53 600
725 620 777 - kontakt@hipermedica.com.pl
Important links
Opening hours
Mon - Fri:
09.00 - 20.00
Saturday:
09.00 - 13.00
Sunday:
Close
© 2023 HiperMedica. All rights reserved.
